Important International Alliances
Our globe is demarcated into nations, states, or countries surrounded by boundaries.
We often get confused by the terms of a nation, a state or a country.
Amazon’s Trends
What is meant by a Nation?
A nation is a large body of people united by a common ethnic group, descent, culture, or language, inhabiting a particular state or territory. It shares a distinctive language, religion, and history. It is generally not related to a location or political identity. It may abide by its own legal procedures. Its states should grant the validity of the laws.
What is meant by a State?
It is a nation or territory considered as an independent political unit organized under one government. It legally controls the affairs of its land and people.
What is meant by a Country?
Most commonly the word country is a less formal word of the three. It also means power and identity. It can be of one nation or multiple nations coexist.
Today, there are 5 major International Alliances that change the boundaries of countries, cultures, and languages.
They influence the world in many ways.
They are:
1. North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO),
2. European Union (EU): Originated in 1950,
3. Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC),
4. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD),
5. Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
Let us now discuss these 5 alliances in detail.
1. North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO):
It is a military association of European and North American countries. It was formed in 4th April 1949 after the world war with twelve founding members. Its main headquarters are located in Brussels, Belgium.

The United States spends three quarters of NATO’s budget.
NATO has presently 31 member countries that are in Europe and North America.
They are Albania, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Turkey, United Kingdom, and United States.
NATO’s main basis was to implement the North Atlantic Treaty (NAT). It was signed on 4 April 1949 in Washington, D.C. its official languages are English and French.
The main purpose behind its formation was the defense against the perceived threat of Soviet aggression. Later many countries joined in NATO.
The founding members signed the Treaty to protect themselves from the attacks of others.
During the tense period of cold war between USA and USSR (Union of Soviet Socialist Republics), it aimed to check on the threat posed by the latter’s.
Bosnia, Herzegovina, Sweden, Georgia and Ukraine are interested to join NATO.
2. EU (European Union): Originated in 1950.
It is a continental union headquartered at Brussels. Six countries (called Inner Six) founded EU in 1948. They are Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany. 22 other countries joined EU between 1973 and 2013.
Now it has 27 members.

They are:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, and Sweden.
It is headed by mixed intergovernmental directorial parliamentary confederation. Its main currency is Euro.
It has 3 main languages (English, French, and German) and 24 official languages. It is growing as an emerging superpower.
Eight countries (Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Serbia, Turkey and Ukraine) are recognized as membership candidates.
Georgia and Kosovo have submitted their applications and are officially recognized as potential candidates.
3. OPEC (Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries):
It is a Cartel type organization. It was founded on 14 September 1960 by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela (five founding members) in Baghdad. Its headquarters shifted to Vienna, Austria in 1965.
Now it has 13 countries as members.
They are:
Algeria, Angola, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, the Republic of the Congo, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Venezuela.
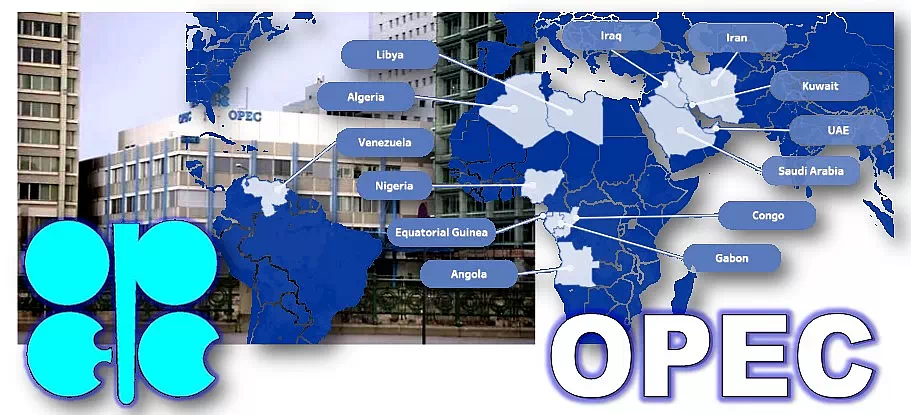
Its official language is English.
Former OPEC members: Ecuador, Indonesia, and Qatar.
OPEC+ is a now a dominating global crude oil group formed in 2016.
OPEC+ 10 members:
In addition to the old 13 member states 10 more countries such as Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan and Sudan are now members.
Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan, and Sudan.
The chief executive of OPEC is OPEC’s secretary general and its conference (supreme authority of OPEC) is headed by the ministers of member countries.
Its budget is shared equally by its member countries. Half of the world’s oil production is accounted by the OPEC’s members.
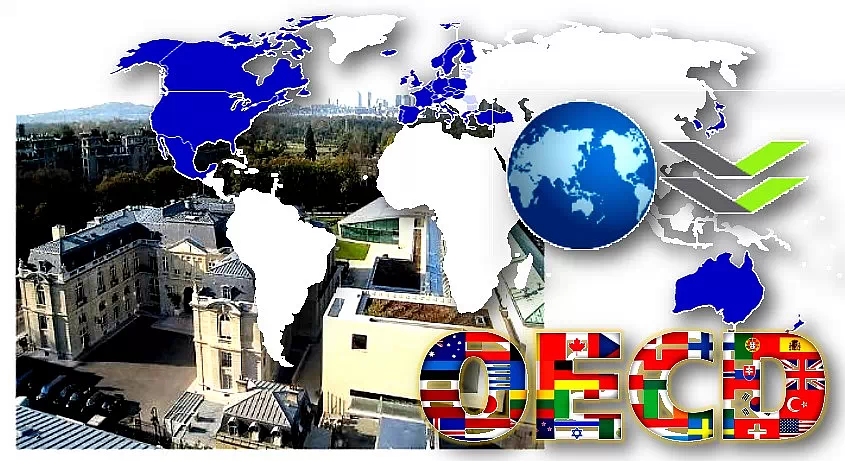
4. OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development):
It was formed in 1961 by superseding the OEEC (Organisation for European Economic Co-operation – established in April 1948) with a main concern to accelerate world trade and economic progress.
It has two official languages i.e. English and French.
It is an intergovernmental organization located at Paris, France. It has now 38 countries as members.

They are:
Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey, United Kingdom, and United States.
The regular minister-level meetings are held to discuss issues relevant to its charter, member countries, and non-member countries for multinational cooperation.
It publishes highly influential data in the form of books, reports, statistics, working papers, and such reference papers and are available at OECD iLibrary. It is an official UNO (United Nations Organization) observer.
5. ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations):
10 countries are the present members.
It was formed on 8 August 1967 in Jakarta, Indonesia.
Initially it was formed by 5 countries as founding members. They are Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
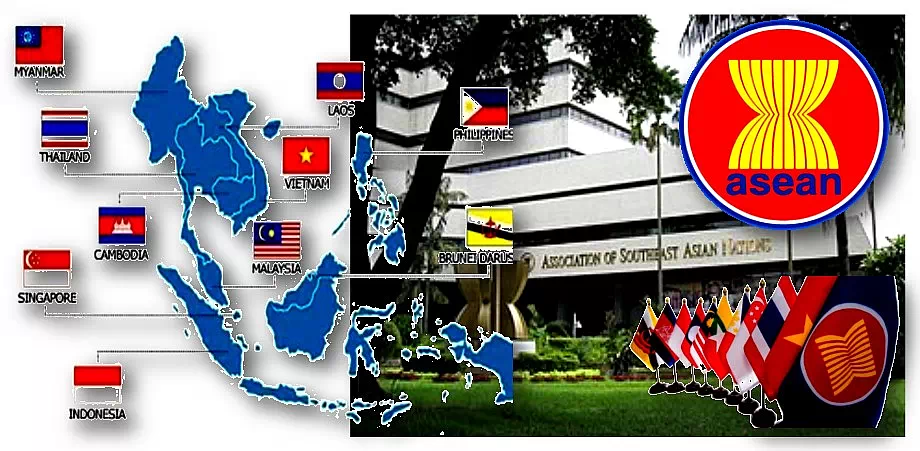
Later 5 more countries joined the ASEAN. So, now it has 10 members.
6th member: Brunei joined as the 6th member on 7 January 1984.
7th member: Vietnam became the 7th member on 28 July 1995.
8th & 9th members: Laos and Myanmar (Burma) joined on 23 July 1997.
10th member: Cambodia joined on 30 April 1999.
It was set up to stimulate the economic and social progress. It promotes cultural development and regional peace.
Its working language is English. Other 11 languages such as Burmese, Chinese, Filipino, French, Indonesian, Khmer, Lao, Malay, Tamil, Thai, and Vietnamese are treated as official languages for contacting states.
It has now become the leading voice on regional trade and security issues.
Papua New Guinea and East Timor have now observer status and are interested to become members of ASEAN.




