FF / Part-05

1. Why do our head gets down first when falling due to fainting?
Fainting is called hypoxia.
This happens if there is not enough supply of oxygen to the brain.
The brain function is especially reliant on oxygen.

Our brain uses more than 25 percent of the body’s oxygen supply (20% at resting stage).
This brings the head closer to the ground, which serves to take advantage of gravity and allow blood to flow more rapidly to the brain.
Continued hypoxia lasting more than a couple of minutes can cause permanent brain damage.
2. Flight surgeons are the physicians trained in aerospace medicine.
Aerospace medicine deals with aviation medicine (for atmospheric flights) and space medicine (for space flight).

This medical science is specialized in dealing with the problems encountered in flight both in atmospheric flight and space medicine.
Physiologist Paul Bert invented this branch of science and regarded as the ‘Father of Modern Aviation Medicine’. He began researching on this branch of science during World War II.
The first unit for space research in the world was established in the US.
3. Blood issuing from the heart can travel down to the person’s toes and back to the heart in just a minute even in a resting time.
Researches on blood supply to our body organs show that:
- Specific organs in our body require 64.7% of the blood from heart called cardiac output (CO).
- The remaining 35.3% of blood flow to be supplied to the distributed organs.
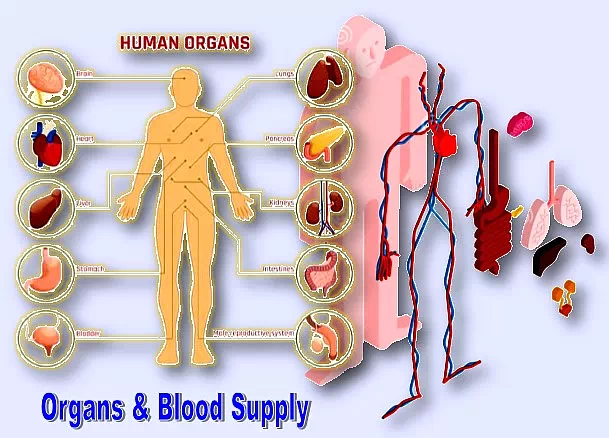
Organs can be classified as two major types:
1. Specific Organs:
Heart, Brain, Eyes, ears, nose, tongue, stomach, and so on that are specified to a boundary.
2. Distributed organs:
The muscles, bones, nerves, fascia and skin that are distributed throughout the body.
4. In the human body the primary organ for digestion and absorption of food is the small intestine.
Humans like all living things take nutrients from food and this process is called digestion (metabolism).
The digestive system is made up of primary and secondary organs (or accessory organs).
- The primary organs:
The mouth, oesophagus (esophagus), stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
- The secondary organs:
The liver, pancreas, salivary glands, and gall bladder.

The primary organs of the digestive system communicate with other organs of the body.
In this process, all chemical interactions necessary for digestion are enabled by the secondary organs.
The main function of the intestine is to absorb nutrients (vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) and water from food and to supply them to the body.
The small intestine is called antrum and begins from the lower portion of the stomach and the end portion of it is connected the large intestine.
The diameter of small intestine is approximately 2.5 cm (1 inch) and its length can be over 3 meters (10 feet) in adults.
5. As little as 10–15 percent of the iron we eat in food is absorbed into the human body.
Iron is a mineral and crucial to the development of haemoglobin (hemoglobin) in the blood.
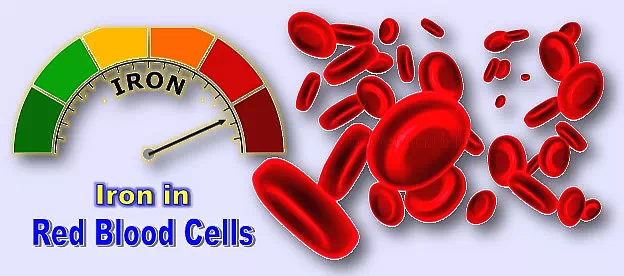
The absorption of iron in the digestive process:
In case of an adult male: Only 10% of the available iron is absorbed.
In case of an adult female: 15% is absorbed.
Iron present in animal flesh is more easily absorbed.
Absorption of Iron originated from plant material (vegetables) is comparatively hard.
6. Human Body has two communication systems:

The nervous system:
- This system communicates through electrical impulses traveling throughout the body as part of a nerve network.
The endocrine system:
- It communicates through chemicals called hormones, which travel through the bloodstream.
7. Every minute, dead skin cells between 30,000 and 40,000 drop off the body.
Skin is the body’s best protector.
New skin cells are always being produced and older cells are forced to the skin’s surface.
This process is called mitosis. It occurs in the innermost layer of skin, medically known as the stratum germinativum.
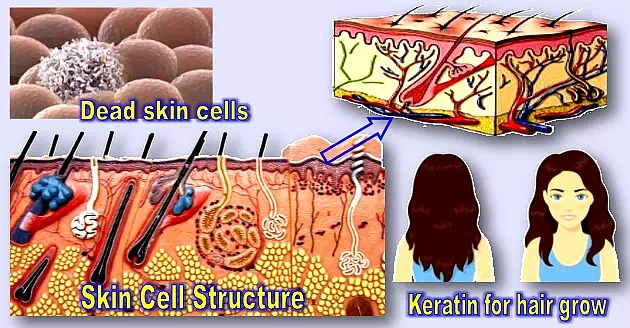
Keratin is produced by the new cells. Keratin is a fibrous protein useful to form outer layer of the skin, hair, nails, feathers, horns, and hooves.
The dead cells still have keratin and it forms layer called waterproof statum corneum layer. This layer makes our body waterproof. It prevents evaporation of water inside the body, and also prevents water from entering the body through the skin.
8. About 40% to 50% of body heat is lost through the head during winter.
That is the reason people wear hats in winter or cold regions. Hats keep the body warm in cold conditions.
Our body temperature remains steady at 98.60F (370C).

People generally get hot when they exercise or use their muscles heavily.
In fact, our body temperature is regulated by the hypothalamus gland. It is located at the base of the brain.
This is perhaps one of the reasons in dense winter or in cold countries, people wear caps/hats.
9. People live in extreme altitudes have more red blood cells (almost 50% more) than the people live at normal heights.
Number of blood cells in our body directly varies in proportion to the altitude.
Red blood cells are also known as erythrocytes. These are responsible for gathering and transporting oxygen and nutrients to the body tissues. In addition, they dispose the tissue’s waste products.

About 175 billion red cells per day are made in the red (bone) marrow and released according to the demands of the body. Haemoglobin is the chemical compound that imparts red colour to the red blood cells.
10. There is estimated approximately 60 to 70% of our body is comprised of water.

The water we take play three main roles in our body:
- Solvent:
Many substances such as nutrients and other vital components can dissolve in it and be transported throughout the body. Thus it supplies the dissolved energy (glucose) to tissues and collects wastes in return to eliminate them.
- Lubricant:
Like a lubricant it prevents friction between various surfaces inside the body, such as bones and blood vessels.
- Temperature regulator:
As temperature of water does not change quickly so that it makes our body stay at a fairly constant temperature.
All Blogs & Vlogs from mamlabs.net

