1. The rhinoceros beetle is the strongest animal and is capable of lifting 850 times its own weight.
Rhinoceros beetle have horns like rhinoceros and so named as rhinoceros beetle. They are herbivorous. The adults eat fruit, nectar, and sap. The larvae feed on decaying matter of plants. They are the largest beetles in the world because they can grow up to 15 cm (6 inches). They are found everywhere in the world except Antarctica.
Amazon – The Fittest

Without any problem in movement or speed, adult of some species can carry 30 times their own weight. Their lifting capacity with some trouble in speed ranges from 100 to 850 time their own weight that makes them the strongest animal in the world. To win the right to mate with females, male beetles fight with other males. They use their horns to drive away the other males off the females. Female beetles lay about 50 eggs.

Their life-span varies from 1 to 2 years. They spent much of their life in larvae-stage. During day time they hide in leaf litter, plants, and fallen logs.
2. The average cough comes out of your mouth at 60 miles (96.5 km) per hour.
Cough is a sudden noisy expulsion air from lungs and is common symptom of upper respiratory infection, bronchitis, pneumonia, or tuberculosis. It clears the air passages.
The average speed of cough is around 96.5 km (60 miles) per hour. Sometimes cough reaches an incredible speed of 100 km to clear the unwanted irritants of the breathing passage ways.
There is nothing to worry about a normal cough. But it can be a sign of medical condition when it lasts for longer time or that produces discolored or bloody mucus.
Coughs are generally two types – acute or chronic.
Acute coughs are general and last for less than three weeks. They are mostly associated with a cold, flu, or bronchitis.

Chronic coughs commonly lasts from 4 to 8 weeks. It leads to fatigue and rarely comes with blood. The common causes for chronic coughs are allergies, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), chronic bronchitis, smoking, throat disorders, and other lung conditions.
3. 11% of the world is left-handed.
The handedness can be defined as ‘the preferred use of the right hand, the left hand, or one or the other depending on the task.
The right and left handedness is generally related to differences between the right and left halves of brain.
The right hemisphere controls movement on the left side of the body. The left hemisphere controls the movement on the right side of the body.
In humans handedness can be of four types.
1. Right-handed, 2. Left-handed, 3. Ambidextrous, and 4. Cross-dominant or mixed-handed.
- Right-handed:
They prefer to use right hand for most fine manual tasks. About 90% of humans are right-handed in the world.
- Left-handed:
They prefer to use left hand for most fine manual tasks. About 10-11% of the population is left-handed.

- Ambidextrous:
They can use both the right and left hands with equal dominance. Less people are ambidextrous.
- Cross-dominant or mixed-handed:
Very less people are cross-dominant or mixed-handed. They have a motor skill manifestation favoring one hand for some tasks and the other hand for doing other tasks.
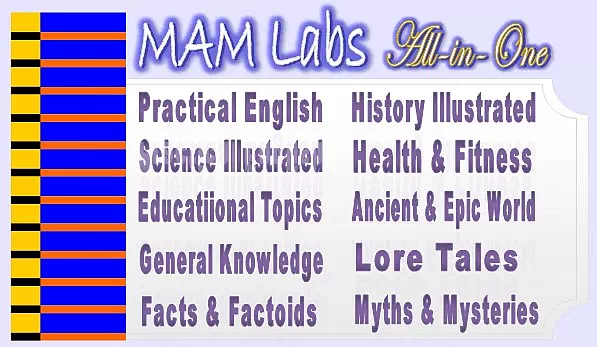
4. Human thigh bones (femurs) are stronger than concrete.
Thigh bone (also called as femur bone) is one of the main associate bones of hip joint. It is exposed to different forces during standing, walking, running, or jumping. The impacts generally act on thigh bone are tensile, compression, torsion, shear, and bending.
The average adult male thigh bone is 48 cm (18.9 in) long and having 2.34 cm (0.92 in) diameter. The thigh bone supports most of the upper weight of the body. Its structure is composite with cortical, cancellous and bone marrow cavity.
The strength of the thigh bone is extremely variable with respect to the different regions depending on its matrix and hardness.
It is the longest, heaviest, and strongest bone in the body. It is able to support up to 30 times the weight of the body. It is proved to be stronger than concrete.
5. Only female mosquitoes bite – Why?
For reproduction, female mosquitoes bite people and other animals for blood meal. They need protein from the blood for the development of eggs. Male mosquitoes do not bite. They feed on plant sap, flower nectar, and water.
To suck up the blood, female mosquitoes uses proboscis (a special mouth part for piercing the skin). At the same time it injects its saliva into the skin that causes itching and resulting in a bump on the skin. Diseases such as malaria, dengue, and so on can only be transmitted by female mosquitoes.
Female mosquitoes continue to bite until they are full. After consuming enough blood, they take rest between two to three days before the process of laying eggs.

Mosquitoes hate certain natural scents like peppermint, cedar, cinnamon, lemongrass, citronella, catnip, patchouli, lavender, and more.
Average life span of male mosquitoes are 6-7 days and female mosquitoes of about 6 weeks. With enough food supply females can live up to 5 months or longer.
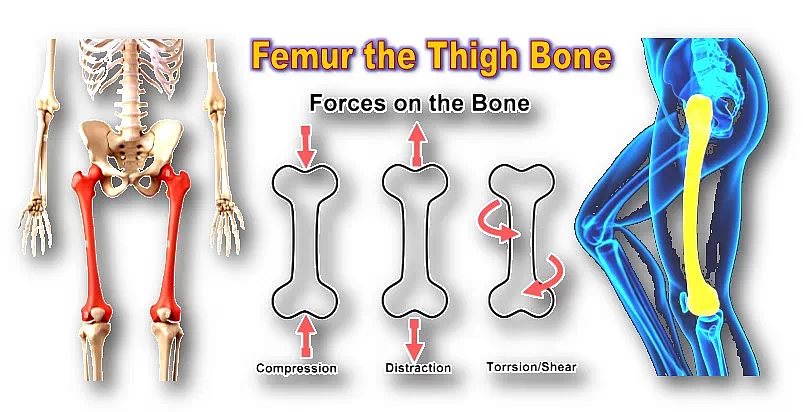
6. While taking rest, the left ventricle pumps about 4–7 liters of blood every minute. The amount can rise to almost 30 liters per minute in a well-trained athlete while doing strenuous exercise.
The heart has four chambers – two atriums (atria) and two ventricles. The upper parts are known as atriums and the lower parts, the ventricles.
Though the heart is a single organ, it acts as a double pump. The right side chambers (right atrium and right ventricle) work as the first pump.
The right atrium receives deoxygenated (oxygen-poor) blood from other body parts. This blood goes to the right ventricle and is pumped to the lungs with the help of pulmonary valve.
After purification, lungs sends the oxygen-rich blood to the left atrium of the heart. The left atrium pumps this oxygen-rich blood to the left ventricle with the help of mitral valve. Thus the left atrium and the left ventricle work as the second pump.
The left ventricle supplies this pure blood to the rest of the body parts.
This whole process is called the circulatory system.
The blood circulation is of two types. 1. Pulmonary circulation; 2. Systemic circulation.
The pulmonary circulation is a short loop connecting the heart with the lungs.
The systemic circulation carries blood from the heart to all the other parts of the body and back again.
The same amount of blood is pumped by the both ventricles. But, a greater pressure is generated by the left ventricle to overcome the greater resistance in the systemic circuit.