Today, in food sector, the demand for ready-to-eat food has been increasing day by day due to the fast-paced life style and increased awareness of quality and nutrients among consumers.
This tendency is undoubtedly putting a lot of pressure on food processors especially who are engaged in fruit and vegetable sector.
Moreover, shelf life of food products has significant effect on the food chain sector.
Short shelf-life will also have adverse effects on the income of growers, processors, retailers and consumers as well.
The fact is that fruits and vegetables are perishable. They deteriorate so quick some few days after harvest.
Food losses around the world are estimated about 40-50% for agricultural products especially for fruits, vegetables, and root crops.
- This means roughly half of the agricultural food production is wasted every year. Therefore, extending the shelf life of agricultural products after harvest is a very important aspect.
Food processing technologies have advanced to meet the evolving magnitude and complexity of the global food system.
Unfortunately, these advanced food processing methods also have some negative externalities in relation with food safety and security.
At the same time, keeping food products afresh for some months without losing the taste and colour is a tough task for the food processor and retailer.
Most important one is to retain the basic vitamins of the food products during post-harvest handling, commercial processing, distribution, storage and preparation.
Concerning all these factors the decisive thing of a food product is – “shelf life,” in other words ‘storage life’.
Shelf life (storage life) is the labelled period on the food product before the date of which it has to be consumed.

As per agricultural products, the shelf life is a vital factor because they are highly perishable.
The main and practical problem in managing good shelf life for agricultural products is the lengthened transport chains.
Moreover, food processing for good shelf life of products requires technologies, investment, infrastructure, and skill because most of the food processors today are entrepreneurs and agribusiness companies.
Lack of awareness about food processing among the farming community and workers is also a major problem.
Extending Shelf life can also prevent infestation of food due to microbes (mould or pathogens).
Benefits of extending shelf life for food products
- It reduces the wastage of (perishable) agricultural products.
- It ensures brand image by supplying value added products to consumers.
- It stops loss of nutritional properties of food.
- It enhances the ROI (Returns on Investment).
Another key factor to extend shelf life of agricultural products is to enable them to respire by using stored energy and oxygen even after harvest.
Today, many modern techniques are being exercised to extend shelf life of agricultural food.
1. Thermal treatments:
These are post-harvest treatments. They include many cleaning techniques such as hot water dip, saturated water vapour heat, or hot dry air. These treatments kill microbes and insects and delay the onset of fungal decay.

They also stop or slow down the ripening process.
2. Food Fortification:
Food fortification is a modern solution to alleviate specific nutrient deficiencies in developing countries. It involves the addition of measured amounts of nutrient-rich premix containing the required vitamins and minerals to commonly eaten foods during processing.
The best examples are:
- Adding iodine to salt during processing.
- Flour fortification with iron and folic acid.
3. Techniques of edible coatings:
- These are external coatings given to the surface of the fresh food products.
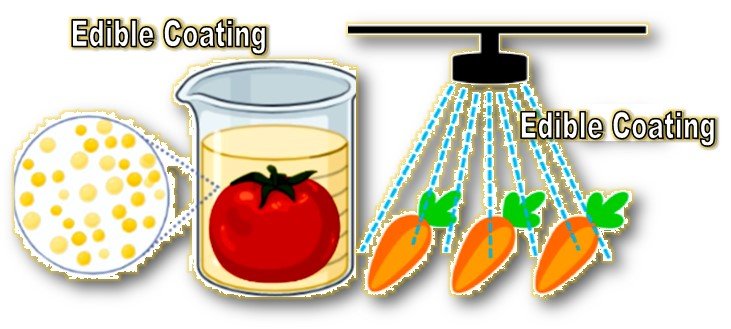
They act as gas barriers by slowing down the aging and oxidation processes. It prevents loss of moisture of the products.
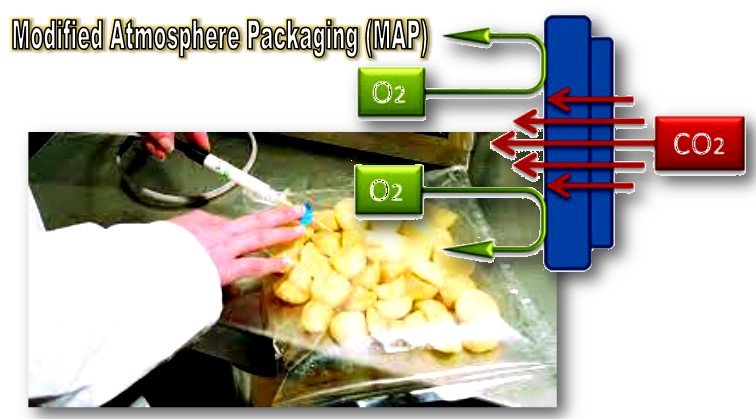
4. Packaging techniques:
The atmospheric air inside a package is substituted with a protective gas. This technique is called MAP (Modified Atmosphere Packaging). The main purpose of MAP is to extend the freshness of food products.
5. Storage techniques:
The atmosphere in the storage room is regulated by these techniques. This type of storage of food products is known as CAS (Controlled Atmosphere Storage). The temperature, and humidity along with the concentrations of oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide are mainly regulated in the storage rooms.

6. Food Supply Chain:
Cold Chain Technology is used in food supply chain. This chain uses an uninterrupted series of refrigerated production, storage and distribution system of food products by adopting unbroken and controlled temperature methods.
7. Using Proper Storage Tools:
Tools such as thermometers, thermos-hydrometers, data loggers, and other packaging devices are used to monitor the temperature and humidity. Certain other devices are also used to measure the firmness and sugar content of the products.

8. Using Proper Packaging Tools:
These tools are generally used to create modified atmosphere in the food pack. In ethylene absorption packaging, additives are incorporated into pallet wraps covering the product boxes.

In a nutshell, the success of producing and distributing a food product with dependable shelf life includes controlling of raw material quality, good manufacturing practice (GMP) for production & packaging, and quality testing of the final product.
The main considering point that a food processor to keep in mind is to supply food products with good shelf life to consumers and thus reducing food wastage.
Moreover, concerns on using proper preservatives and additives to enhance taste and extended shelf life of the product are linked with the food-related illnesses.
For example excessive use of salt and some tasty ingredients may result in obesity and food-related illnesses that will especially have impact on child development.
To minimize all these ill-effects, Climate-smart techniques such as packaging, storage, and supply chain as discussed above in the points 4, 5, and 6, will have the potential to contribute to food safety and security with good shelf life.
So, the application of science and technology in food processing systems should largely focus on delivering safe, tasty, nutritious, abundant, diverse, convenient, less costly products, and durable (good shelf life) in view of the increasing population.
GOOD SHELF LIFE MEANS GOOD QUALITY FOODS

All Blogs & Vlogs from mamlabs.net


